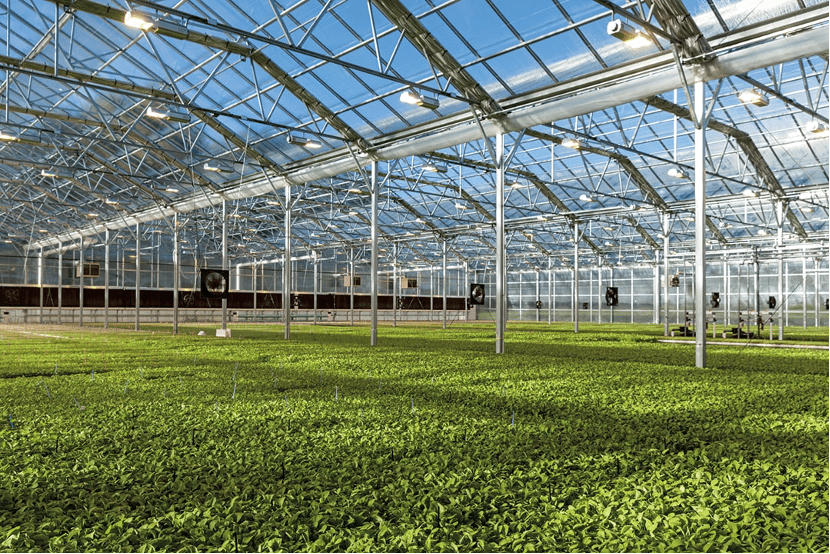
In today’s article, we will tell you the most preferred greenhouse varieties and production methods. But before that, we need to find out what a greenhouse for horticulture is and why it is used.
What is A Greenhouse?
Greenhouses are structures covered with materials such as plastic, glass, or fiberglass, which are built to reduce or control the effects of climatic conditions on ornamental plants and food cultivation. The first greenhouse was built in 1545 by Daniel Barbaro in the botanical garden established by the Republic of Venice (today Italy). In the conditions of that period, the building, which was closed with walls built of stone and brick, also had no windows. Today, some sensitive plants grown in greenhouses (such as cucumbers) were moved into this structure in the winter months and taken to their old places in the spring. Thanks to the advancing technology today, beyond being less affected by climatic conditions; modern greenhouses can be installed through computers, where climatic conditions can be regulated in such a way as to maximize the efficiency of production.
The greenhouse structure is the basic skeleton structure that protects all systems and structures of the greenhouse and firmly supports these structures. All greenhouse steel construction materials produced by our company for you are fast production and high-quality products. We prevent the rust that may occur in the steel due to the humid or water exposure of the greenhouse environment and ensure that your greenhouse has a longer service life.
Other Structures That Create a Greenhouse Effect
Low tunnels are plastic sheeting in the form of elongated half-cylinders of small size. These tunnels are about one meter high and one meter wide, too small to work from the inside. They are ideal for outdoor plants planted in containers or on the ground. They are removed when the plants are ready to grow beyond the tunnel height. High tunnels are larger and longer versions of low tunnels. they are 4-5 meters wide and 2-3 meters tall. They are easy to build, like low tunnels; however, due to the smaller volume, they do not retain as much heat as plastic greenhouses.
Types of Greenhouses
Greenhouse varieties are usually classified according to the way they are installed or according to their structure.
Types of Greenhouses According to Installation Methods: Greenhouses for commercial production can be classified as adjacent, independent(individual), or gutter-connected (block greenhouses) according to the installation methods.
- Adjacent Greenhouses; as the name implies, they are built adjacent to a structure, that is, adjacent to the building. One or several surfaces of adjacent greenhouses are covered with masonry, such structures are called lean to type greenhouses. The slope of the roof faces south and is covered with transparent material.
- The main advantage of greenhouses of this type is that construction costs are lower compared to other types. The joint use of a part of the structure (one wall) with the building will reduce costs.
- On the other hand; since the energy and air conditioning systems in the building can also be used in the greenhouse, the cost will also be reduced here. However, it is very difficult to keep the heat under control. This also comes across as a disadvantage.
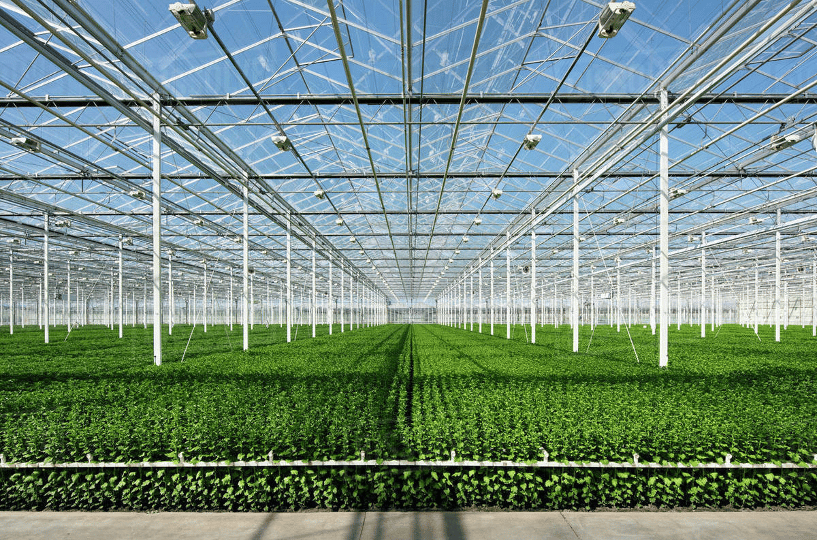

- Independent (Individual) Greenhouse; it is built independently of any other structure or greenhouse. Each independent greenhouse also has its heating, cooling, and irrigation systems.
- Since each independent greenhouse is controlled by a heating/cooling system, it is easier to provide separate environments. One greenhouse can be run warm for propagation, and the other colder for growing.
- Some sections of freestanding greenhouses can be closed to save energy when not in use.
- Multi-pitch greenhouses are best suited for regions with heavy snowfall, as they need heat to melt snow from the gutters.
- It is good for uneven terrain.
- It is easier to build and maintain than block greenhouses.
- Gutter-Connected (Block) Greenhouses; are large interconnected single greenhouses formed by the merger of independent greenhouses. There are usually struts so that the weight of the roof can be carried.
- More cost-effective for areas larger than 2 acres.
- Reduction in heating costs, as the ratio of surface area, to floor area is less. Thanks to the low glazed area, heating costs can be up to 25% less.
- Fancy Greenhouse; a conservatory is a building or room with a glass or other transparent roof and walls used as a greenhouse or sunroom.
- Venlo Greenhouse; the Venlo greenhouse is probably the most well-known type of greenhouse among professional growers.
Types of Greenhouses According to Their Structure:
According to their structure, greenhouses can be classified into four types: Quonset, Gothic, Traditional (with a Gable Roof), and A-Frame.
- Quonset Type Greenhouse: Quonset-style greenhouses are semi-circular structures that look like large, clear barrels that have been cut in half. This structure has a curved roof and a military hut-style design. Pulleys are usually made of aluminum or PVC pipes and glazed with polyethylene film or panels for better insulation. The side walls quite limit the storage space and headroom. It is the cheapest and easiest type to build under most conditions. Quonset-style greenhouses are often used when building individual greenhouses. Installation can be made in the area where it is thanks to the fixtures that pass into each other. Thus, it can be built only, without also needing carpentry skills. On the other hand, since these fixtures can be easily disassembled and installed, you can move your greenhouse as needed.

- Gothic Greenhouses: The design is inspired by the windows of Gothic cathedrals all over the world. It is built with bent walls to form a pointed roof. These greenhouses, which are a derivative of quonset greenhouses; are more durable and have more air space. Compared to traditional greenhouses, they can be built more easily and cheaply. The Gothic arch design is famous for its ability to withstand strong winds and heavy snowfall. The half-teardrop shape of the roof is ideal to allow snow and rain to flow easily and prevent damage from significant precipitation or residue accumulation. The arched roof of the Gothic greenhouse eliminates the need for structural beams. This technique not only helps to reduce costs but also makes construction faster and easier and requires fewer materials.
- Traditional (Gable Roof) Greenhouses: Greenhouses with a gable roof are one of the most common types of greenhouses, because they receive the maximum amount of sunlight, while at the same time providing a large area inside the structure for growing a large number of plants. Thanks to the flat walls and a higher roof, you can walk freely indoors while taking care of your plants on the one hand. The design is quite simple, so you also won’t have much difficulty building it yourself. However; compared to other greenhouse types, its construction requires more effort. Depending on the materials you use for the frame and cladding, the construction costs can also be quite reasonable. The side walls that receive wind will be more affected because they are wider and flatter, but the fact that the structure has a skeleton also makes it more durable. Of course, this situation will also change depending on the materials you use for the frame and cladding.
- A-Framed Greenhouses: Simpler than the gable roof greenhouse, but equally popular, the A-frame greenhouse requires a very small number of materials and can be built quite cheaply and easily. It is a little more difficult to maneuver indoors due to the wide base and narrow apex, and the airflow is often not ideal at low edges and tight corners.
The production processes of all these structures must undergo very strict inspection, and the layout must be quality controlled. As YENA Engineering, we attach great importance to quality control and we do fast and high-quality work. We know that quality products will result in a productive crop and we are working for this.

YENA Engineering offers you a wide range of products. With a commitment to continuously improving brand image, product quality, and service reliability. If you contact our qualified and experienced staff, we will offer quality products and timely support for you.


