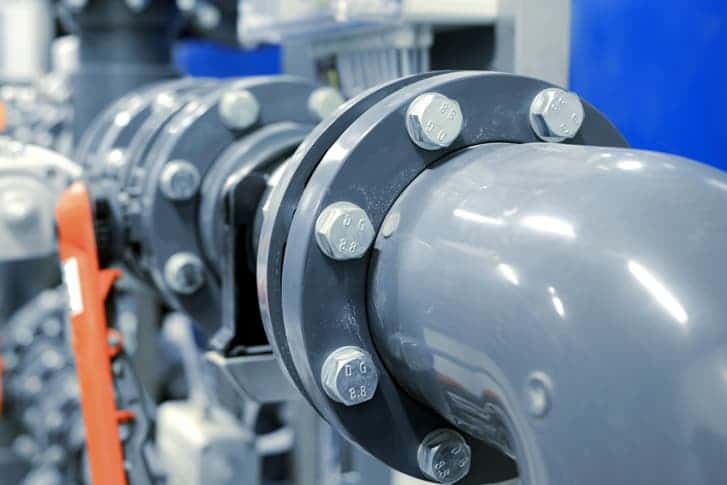
Forged flanges are used as fittings to form a piping network for cylinders, valves, pumps and other equipment. Forged flanges combine two separate machinery parts together. They can be an extension to a structure in order to make the object stronger.
Types of Forged Flanges
Stainless steel flanges come in many different types. Each species meets its special requirements. For example, long weld neck flanges are attached to the necks of the pipes. The welding method of this flange ensures that its thickness is the same as the pipe to which it is attached. These flanges are most commonly used in high-pressure applications. There are also other types of flanges such as Weld Neck Ring Flange (WNRF), Slip-On Ring Flange (SORF), Blind Ring Flange (BLRF), Socket Weld Ring Flange (SWRF), Threaded Ring Flange, Lap Joint Ring Flange (LJRF) and Ring Type Joint Flange (RTJF).

4 Main Production Processes of Flanges
There are four main manufacturing methods of flanges. These are forging, casting, cutting, and rolling.
Casting is a method of pouring molten metal into a casting cavity that conforms to the shape of a flange. After cooling and hardening, the flange cavity can be retained, most of the casting material is initially hard, but when heated to liquid metal, the molding materials can be sand, metal, or even ceramic. On the other hand, forged flanges are one of the flange products with the best mechanical properties. Its raw material is usually a hollow tube, which is then continuously cut and chiseled to prevent segregation, looseness and other ingot defects. The cutting flange produced by cutting the inner and outer diameter and thickness directly out on the steel plate, and then the bolt hole and water line are processed. Finally, the rolling flange is made by cutting the middle plate into strips, then rolling it into circular welded joints and then flattening it.
Production Process of Forged Flange
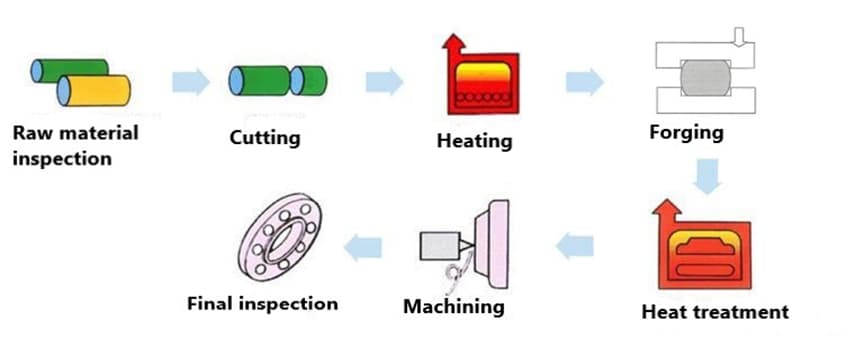
The method of forging typically consists of the following procedures, which are blanking, heating, shaping, and cooling. The method of forging can be classified as free forging or a die forging operation.
Free forging has low productivity and high machining allowance, but the tool is simple and versatile, so it is widely used for forging one-piece and small series forgings with a simple geometry. On the other hand, die forging has the advantages of simple operation, high productivity, mechanization, and automation. Die forgings have high dimensional accuracy, a small machining allowance, and a more reasonable grain structure distribution, which can further improve the service life of flange parts.
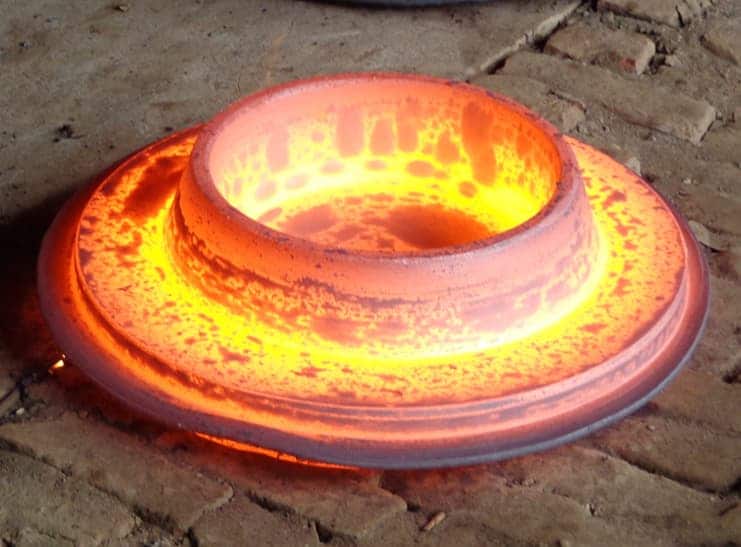

Die Forging
Die forging is also known as model forging. Follows the basic steps: blanking, heating, pre forging, final forging, punching and connecting skin, trimming, tempering and shot peening. Common processes include upsetting, drawing, bending, punching and forming.
The widely used die-forging machineries are forging hammer , hot die forging press, flat forging system, and friction press. The forging flange is normally of higher quality, typically by die forging, the crystal structure is good, the strength is high and the price is of course costlier.
Free Forging
Free forging refers to a method of forging where the heated iron/steel is anchored and then formed by hammering, pressing, or other methods. Free forging can flexibly form the shape of each product and is suited for making large components or for diversified small-quantity production. As mentioned before, free forgings productivity is low and the machining allowance is large, but the tool is simple and the versatility is large, so it is widely used for forging a single piece and a small batch of forgings with a simple shape.
Properties of forged flanges
Forged steel is a material resulting from alloying iron and carbon under extremely high pressure. Forged steel has less surface porosity, a finer grain structure, more tensile and fatigue strength, and greater ductility than any other processed steel. When the steel is heated to forging temperature, it becomes ductile and malleable, allowing it to be molded into the required shape through the application of force and pressure.
The advantages and disadvantages of forged flange
Forged steel flanges have both advantages and disadvantages and these can be described by the following points:
- Forged flanges generally have lower carbon content than cast iron flange, so they are not easy to rust.
- It has a good streamlined shape and compact structure, so their mechanical properties are better than cast flange.
- If the forging process is improper, the grain will be large or uneven, and a hardening crack will occur. The cost of forged steel flanges are higher than the casting flanges.
- Forgings are compatible with higher shear and tensile forces than castings.
- The internal structure of the forging is uniform, and there are no harmful defects such as pores and inclusions that migh appear during casting process.
Forged Flange Applications
Forged flanges play an important role in the petrochemical industry, as this is where a multitude of oil and gas pipelines made up of various components can be found.
Pipelines are systems that are responsible for transporting oil and derivatives such as biobutanol utilizing a system of pumping stations that drive the fluid at an average speed of between 1 and 6 meters per second. Given the complexity and dimensions of their structure, studies on the environmental impact must be carried out before construction. They are centered on steel pipes whose diameter varies from 12.7 mm to 360 cm.
Gas pipelines have the same function, transporting materials, but in this case, the materials are combustible gases, mainly natural gas. They perform this operation at high pressures. The lines are mostly built underground at a depth of one or two meters depending on the terrain, rarely above ground. It is standard practice that shutoff valves are placed at various points in the pipeline to cut off the flow of gas if necessary.
Standards
Standard Forged Flanges (Weld-neck, Slip-on, Socket-weld, and Blind) are manufactured by Yena Pipe to different specifications like ASME, DIN or EN standards. Flanges cover a full range of pressure ratings of these specifications (150 – 2500 psi for ASME & PN6-PN400 for DIN / EN flanges).
For more information please visit: YENA Pipe
You may check also these articles:
What is Forging
Forge Materials And Applications
Types Of Forging

